
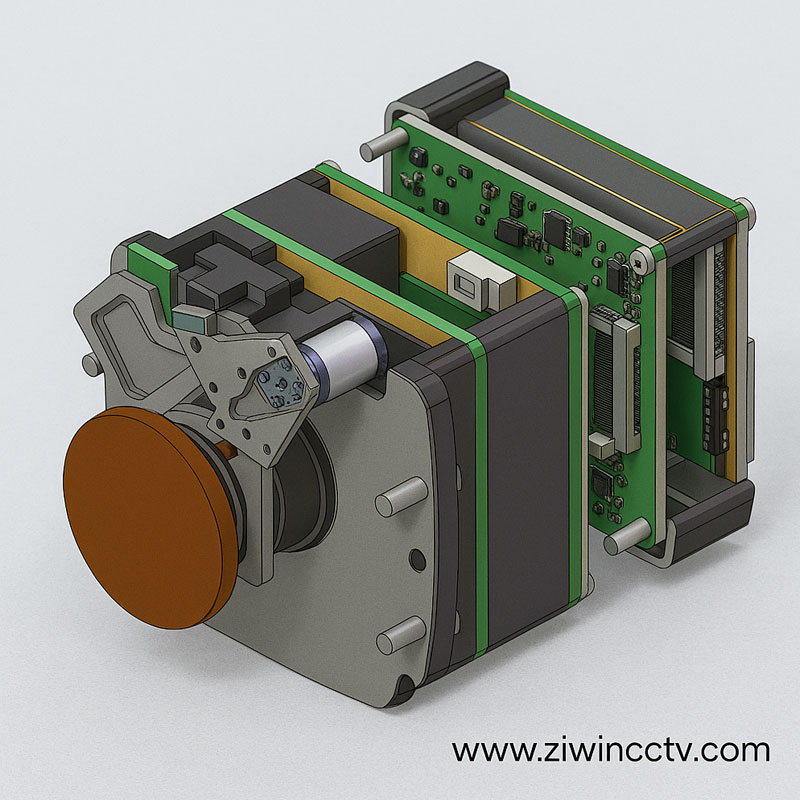
Infrared thermal imaging technology has become a vital tool in security surveillance, border defense, industrial inspection, and firefighting. By detecting temperature differences instead of visible light, it enables reliable imaging day and night, even in harsh weather conditions.
At the heart of every thermal imaging system is the infrared core, which determines image clarity, detection range, and overall performance. Infrared cores can be broadly divided into cooled infrared cores and uncooled infrared cores.
So, what’s the difference between the two? And which one is best for your application? Let’s take a closer look.
Cooled infrared cores use a cryogenic cooling system (such as a Stirling cooler) to lower the detector’s temperature to around -200°C. This cooling process dramatically reduces thermal noise and boosts sensitivity.
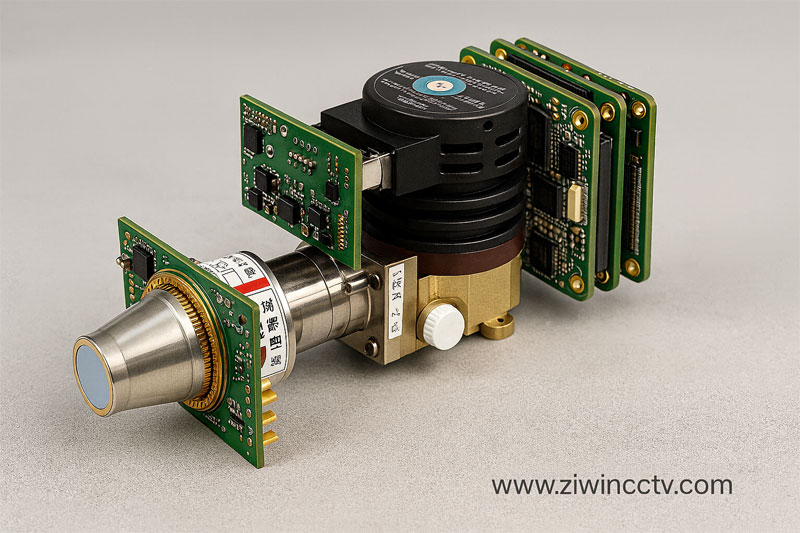

Features
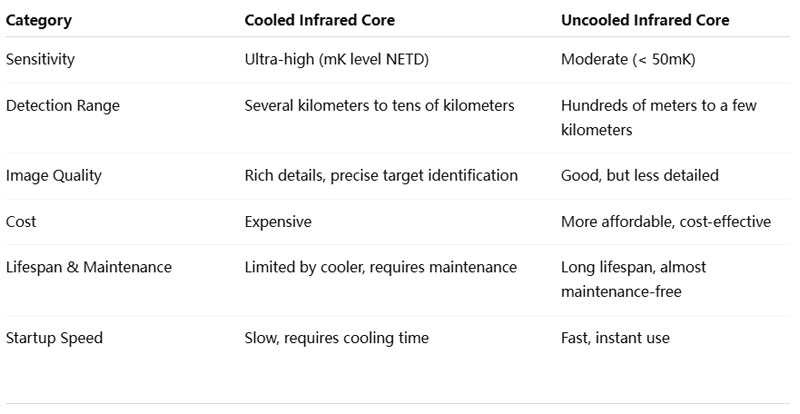
· Ultra-high sensitivity: Capable of detecting extremely small temperature differences (NETD at milliKelvin level).
· Long detection range: Ideal for long-distance monitoring, reaching several kilometers.
· Superior image quality: Delivers sharp details for accurate target recognition.
Limitations
· High cost and complex structure.
· Limited lifespan due to cooler wear (typically a few thousand hours).
· Longer startup time, as cooling is required.
Typical Applications
· Military reconnaissance and border surveillance.
· Long-range maritime monitoring.
· High-precision scientific research and testing.
Uncooled infrared cores use microbolometer detectors, which operate at ambient temperature without requiring cryogenic cooling.
Features
· Compact and lightweight design with lower cost.
· Low power consumption, long lifespan, and almost maintenance-free.
· Instant startup, ready to use without waiting for cooling.
Limitations
· Lower sensitivity compared to cooled cores.
· Shorter detection range, mostly for medium- and short-range monitoring.
· Less detailed image contrast.
Typical Applications
· Industrial inspection and electrical utility monitoring.
· Firefighting and emergency response.
· Security surveillance and automotive night vision.
· Choose a cooled infrared core if you need extreme sensitivity, ultra-long detection range, and high-end performance (e.g., defense, border control, scientific research).
· Choose an uncooled infrared core if you prioritize cost efficiency, reliability, and flexible deployment (e.g., industrial inspection, firefighting, security monitoring).
At ZIWIN, we specialize in heavy-duty PTZ platforms integrated with thermal imaging cores, delivering reliable monitoring in complex environments:
· Heavy-duty PTZ: Supports long-range zoom lenses and thermal imaging cores.
· Corrosion-resistant design: Built for coastal and harsh weather conditions.
· Flexible core integration: Compatible with both cooled and uncooled infrared cores to fit diverse needs.
With ZIWIN’s solutions, customers gain all-weather, long-range, and stable surveillance capabilities for mission-critical applications.
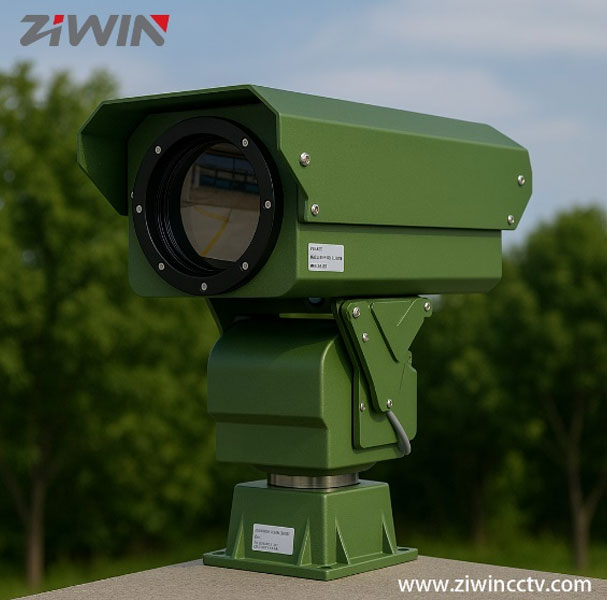
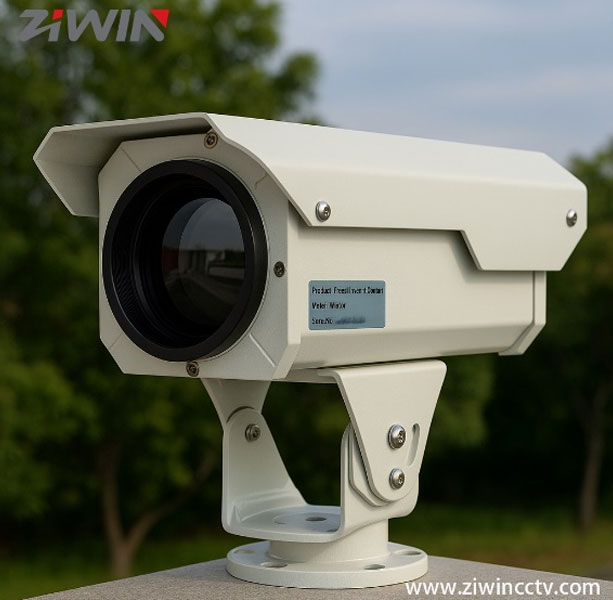


There is no absolute “better” option between cooled and uncooled infrared cores — it depends on your application:
· Cooled cores offer unmatched sensitivity and long-range performance.
· Uncooled cores provide cost-effective, versatile solutions for mainstream use.
By understanding the differences, you can make the right choice for your specific project.
For customized thermal imaging + PTZ solutions, contact ZIWIN to learn more sales@ziwincctv.com

Ziwin CCTV Cameras have a high quality. If you are interested in our products, please leave a message here, we will respond as soon as possible.